Sonification of images
Motivation
One of the main barriers encountered by blind people is access to graphic information, including photos, maps, drawings and pictures. There is a need to develop effective methods for processing visual information into sensory signals that are accessible to blind people. This work concentrates on expanding and acquiring new knowledge in the field of presentation of visual scenes for the blind using the senses of touch and hearing. The research hypothesis is as follows: it is possible to develop tactile-controlled sound patterns allowing the blind user to correctly interpret the image displayed on the touch screen.
- Research directions
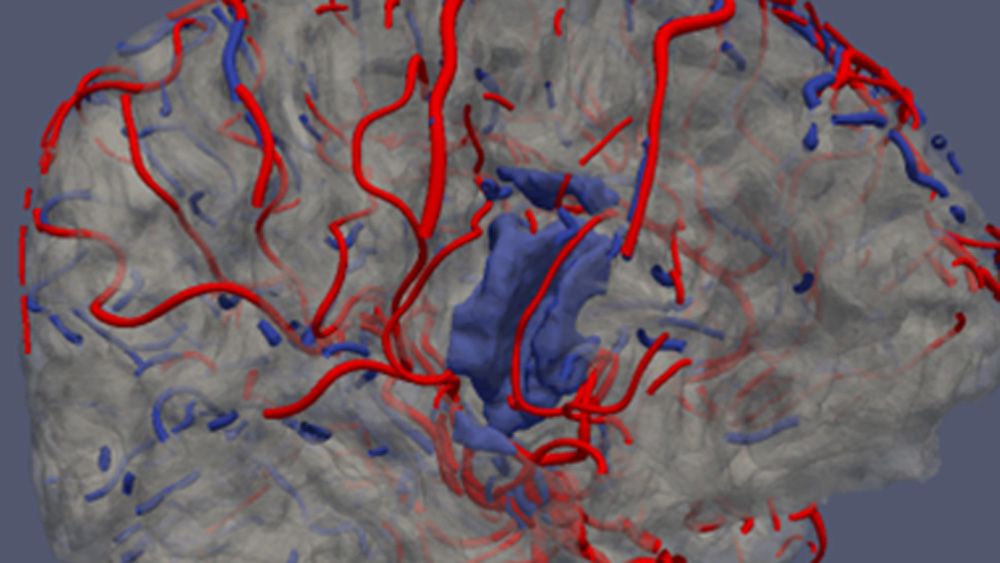
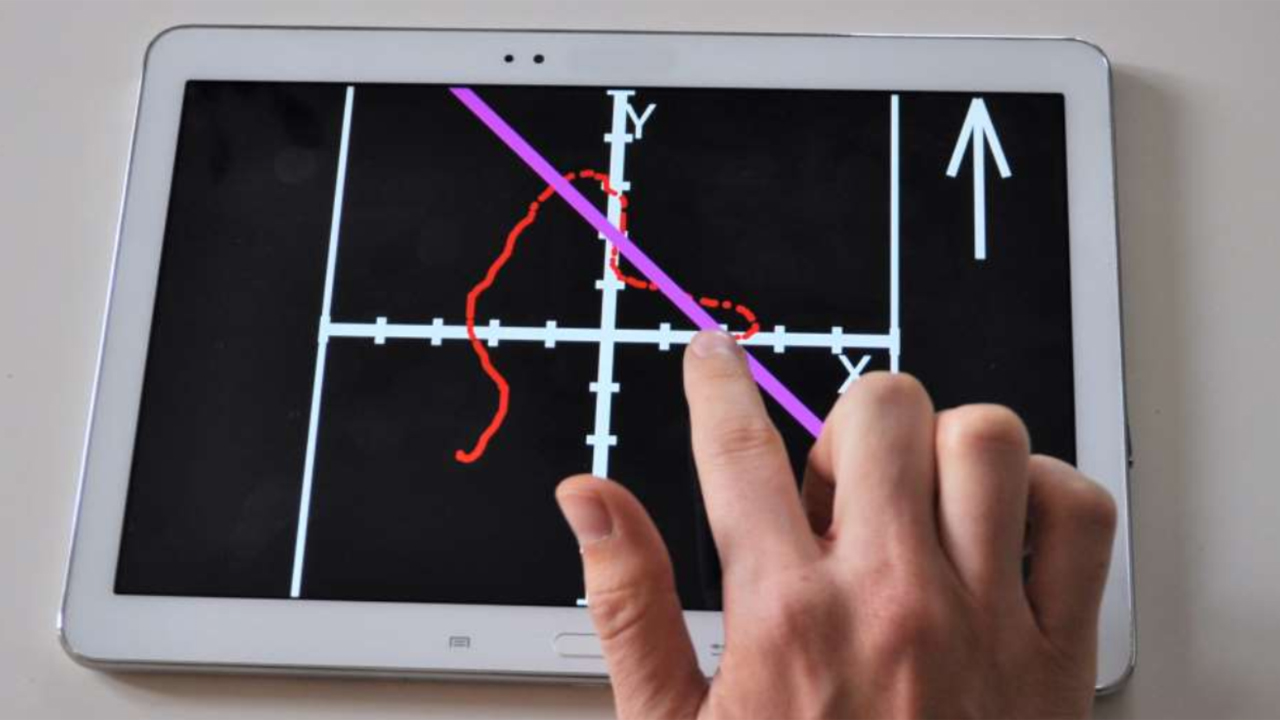
A unique set of algorithms are being developed to covert images into sounds. The sonic space is understood as a combination of a number of sound parameters such as volume, fundamental frequency, timbre (i.e. the shape of the sound spectrum), modulation amplitude and frequency. The developed procedures will allow a selection of audio parameters to be used to map local image features (brightness, colour, texture) and spatial characteristics (shape, size, location and spatial relations). When representing the spatial characteristics covering a larger area of interest in the image, we utilize techniques for building so-called “auditory scenes” according to psychoacoustic theories of auditory streams described by Bregman. This approach is particularly important in auditory presentation of images of 3D scenes.
- Achievements
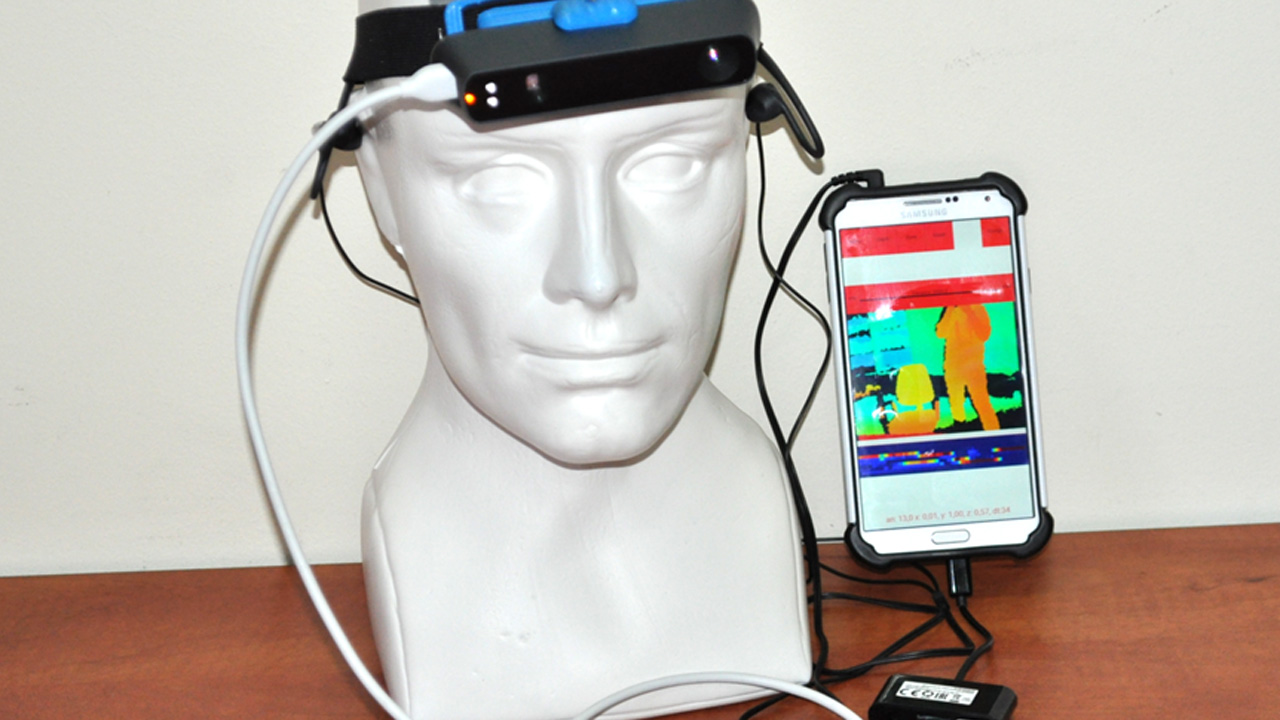
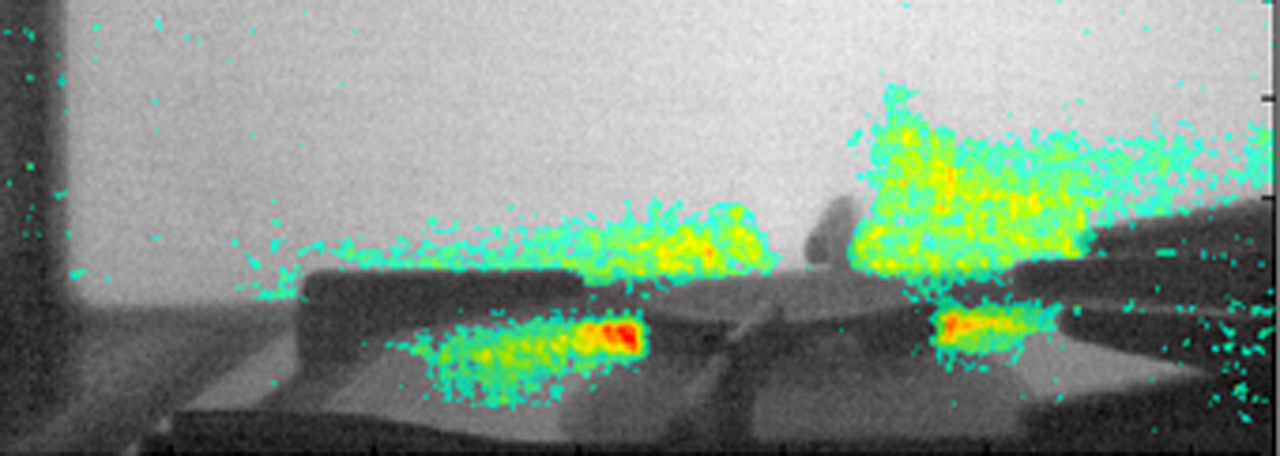
An original interactive sonification techniques for the purpose of 3D scene representation for the visually impaired people were devised, implemented and tested. The techniques were tested by visually impaired users who managed to successfully perform indoor mobility tasks. The system’s usefulness was evaluated quantitatively by means of system usability and task-related questionnaires. We have also shown that the proposed sonification techniques can be a viable tool in the learning process of blind children, in particular such subjects as: geometry, anatomy and geography.
- Perspectives
The expected impact is the development of conceptual basis for unique human-computer interaction systems with a particular focus on the blind. The performed research allows to determine methods of translating visual information into auditory cues that will enable interactive, touch-auditory perception of images with the greatest efficiency. A far reaching goal is to work out effective sonification schemes that will aid the blind in mobility and navigation.
- Contact persons
- Dr. Michał Bujacz
 , e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
, e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
- Dr. Piotr Skulimowski
 , e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
, e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
- Dr. Andrzej Radecki
 , e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
, e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
- Prof. Paweł Strumiłło
 , e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
, e-mail: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
- Dr. Michał Bujacz
- Relevant publications
- Radecki A., Bujacz M., Skulimowski P., Strumillo P., Interactive sonification of images in serious games as an education aid for visually impaired children, British Journal of Educa-tional Technology, 2019, DOI: 10.1111/bjet.12852
- Skulimowski P., Owczarek M., Radecki A., Bujacz M., Rzeszotarski D., Strumillo P., In-teractive Sonification of U-depth Images in a Navigation Aid for the Visually Impaired, Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces, 2018, DOI: 10.1007/s12193-018-0281-3